m a n a g e m e n t ' s d i s c u s s i o n a n d ANALYSIS
reGulation, policy & direction
In Ontario, the Ministry of Energy (Ministry) sets the overall policy for the energy sector, guided by relevant laws and regulations.
The Ministry oversees the IESO and the Ontario Energy Board (OEB), which regulate the energy sector as set out primarily in three statutes — the Ontario Energy Board Act, 1998 (OEB Act); the Electricity Act, 1998; and the Energy Consumer Protection Act, 2010.
The OEB Act establishes the authority of the OEB to approve and fifix all rates for the transmission and distribution of electricity in Ontario and to set standards of service, conduct and reporting that must be adhered to as a condition of being licensed.
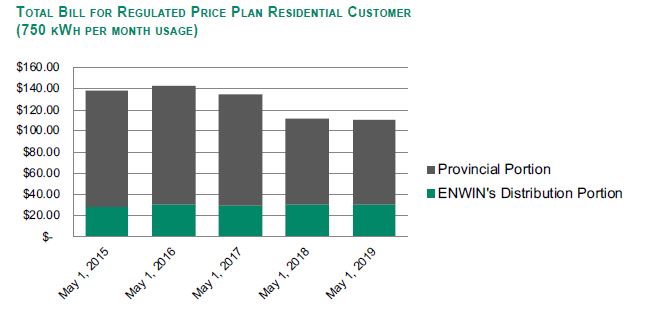
The OEB's regulatory framework for electricity distributors is designed to support the cost-effective planning and operation of the electricity distribution network and to provide an appropriate alignment between a sustainable, financially viable electricity sector and the expectations of customers for reliable service at a reasonable price.
The OEB typically regulates electricity rates for distributors using a combination of detailed Cost of Service (COS) reviews and Incentive Regulation Mechanism (IRM) adjustments.
combination of detailed Cost of Service (COS) reviews and Incentive Regulation Mechanism (IRM) adjustments. Under the OEB's rate-setting methods, actual operating conditions may vary from forecasts, such that actual returns achieved can differ from approved returns. Approved electricity rates are generally not adjusted as a result of actual costs or revenues being different from forecast amounts, other than for certain prescribed costs that are eligible for deferral for future collection from, or refund to, customers.