Section 2 – The Community Safety and Well-Being Planning Framework
The community safety and well-being planning framework outlined in this section will help to guide municipalities, First Nations communities and their partners as they develop their local plans. It is crucial for all members involved in the planning process to understand the following four areas to ensure local plans are as efficient and effective as possible in making communities safer and healthier:
1. Social Development;
2. Prevention;
3. Risk Intervention; and
4. Incident Response.
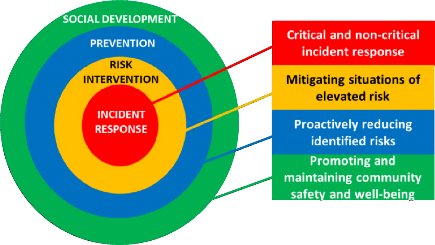
Social Development Promoting and maintaining community safety and well-being
Social development requires long-term, multi-disciplinary efforts and investments to improve the social determinants of health (i.e., the conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age such as education, early childhood development, food security, quality housing, etc.) and thereby reduce the probability of harm and victimization. Specifically, social development is where a wide range of sectors, agencies and organizations bring different perspectives and expertise to the table to address complex social issues, like poverty, from every angle. The key to successful social development initiatives is working together in ways that challenge conventional assumptions about institutional boundaries and organizational culture, with the goal of ensuring that individuals, families and communities are safe, healthy, educated, and have housing, employment and social networks that they can rely on. Social development relies on planning and establishing multi-sectoral partnerships. To work effectively in this area, all sectors need to share their longterm planning and performance data so they have a common understanding of local and systemic issues. Strategies need to be bolstered or put into place that target the root causes of these issues. Social development in action will be realized when all community members are aware of services available to them and can access those resources with ease. Knowing who to contact (community agency versus firstresponder) and when to contact them (emerging risk versus crisis incident) allows communities to operate in an environment where the response matches the need. Communities that invest heavily in social development by establishing protective factors through improvements in things like health, employment and graduation rates, will experience the social benefits of addressing the root causes of crime and social disorder.